
Benefits relating to occupational health management are becoming increasingly important, and not just among Gen Z. Health is an overarching theme that runs through all generations and includes both the Physical health as well as the Mental health of employees. The aim of German companies must therefore be to create a sustainable workplace where employees can work effectively and without risk. This is not just about the obvious dangers, such as toxic substances, heavy production parts or extreme temperatures. It is also about everyday hazards, such as the wrong sitting position at the desk or a lack of water. In the case of psychological stress, the dangers are even more invisible, as everyone reacts differently to external influences such as stress, lack of appreciation or loneliness.
Starting point for occupational health management
Occupational health management Definition
3 pillars of occupational health management in the company
Occupational health management - measures
Digital occupational health management
What does BGM cost and what subsidies are available?
The Journal of Health Monitoring (2021) found that 61.3% of the population suffered from back pain in the last 12 months. 45.7% suffered from neck pain. A non-ergonomic sitting position at work is certainly not the main reason, but a very big driver when you consider that you spend 8 hours a day in this position. It is alarming that both back and neck pain are on the increase at a young age. In the 18-29 age group, over 50% of men and women suffer from back pain.
Musculoskeletal disorders have been a common reason for sick leave for years. In recent years, however, especially since corona, mental illnesses have increased significantly and were sometimes even responsible for more sick days. In 2012, employees were on sick leave for an average of 2.46 days with a mental health diagnosis. In 2022, however, it was 3.33 days. This is a huge increase and companies should keep an eye on mental health.
Occupational health management therefore represents an absolute competitive advantage for many companies and at the same time it has been recognised how important the health of employees is for the profitability of the company. Nevertheless, according to the IFBG study #whatsnext - Working healthily in the hybrid world of work Not all companies have implemented successful health management by a long way.
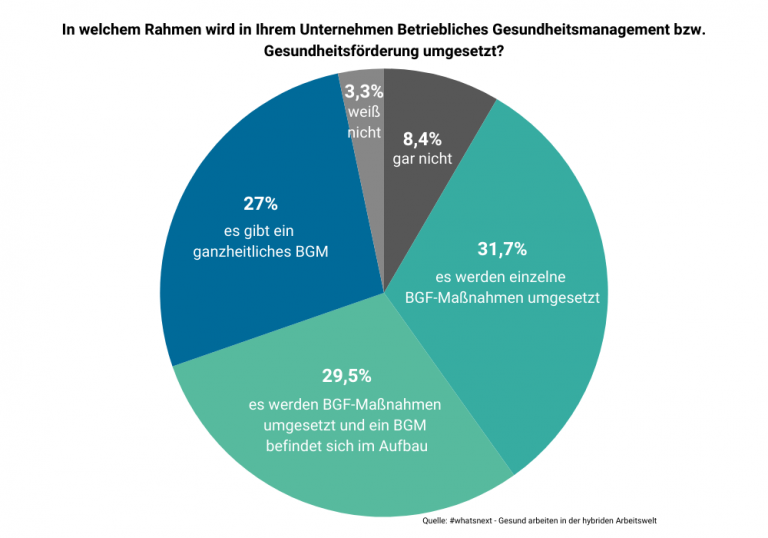
The approaches are just as different as the companies that use them. But they all have one thing in common: Employees take centre stage! Let's take a look, what occupational health management involves and how to implement it.
Occupational health management is a holistic approach that combines all processes to promote the health and well-being of employees. This means Behavioural and situational prevention must be considered. The overarching goal is to improve the health of employees in the long term and thus minimise the Reduce sickness rate.
It's all about employee health. But successful occupational health management is so much more than just the annual health day in the company. By definition, occupational health management encompasses three areas within the company: Occupational health and safety (OH&S), workplace integration management (WHM) and workplace health promotion (WHP).
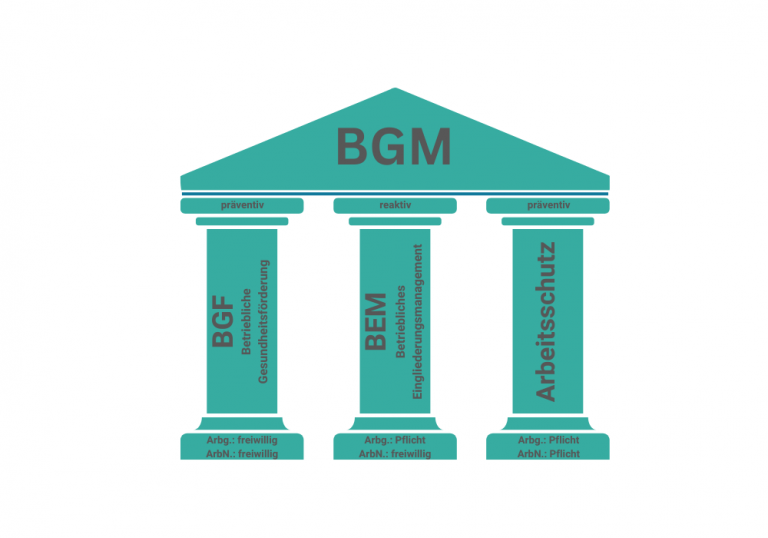

Every employer in Germany is obliged to implement and comply with the statutory regulations on occupational health and safety, which can be found primarily in the Occupational Health and Safety Act (ArbSchG). The work, the working conditions and the workplace must be organised in such a way that risks to life and health are avoided as far as possible.
The most important component of the AUG is the Risk assessment. However, it is important that not only physical integrity is taken into account, but also mental health. In most cases, this analysis is carried out by an occupational health and safety specialist. However, digitalisation and the development of artificial intelligence are opening up new possibilities here. These Digital solutions for risk assessment are particularly suitable for employees working from home. In principle, it does not matter whether a company uses a person or a device for the implementation. The result must be a healthy workforce.
Of course, no company wants employees to fall ill. However, even with the best efforts, this cannot be completely avoided. Employees who, in certain cases that could not be avoided, do fall ill and are absent for a longer period of time (more than 42 days within 12 months) must be be reintegrated after their return. At the same time, it must be ensured that these employees do not fall back into incapacity for work. BEM is particularly important in the case of psychological problems, but also in the case of long-term absences due to physical complaints.
The workplace health promotion is voluntary in contrast to the other two BGM pillars, but is almost more important as the measures can be customised. Employers have the opportunity to strengthen the topic of health in the company by offering a wide range of measures. Basically, it can be said that these measures serve behavioural prevention and prevent absences. These include, for example, measures to
Some measures are even subsidised or tax-exempt. In general, these measures offer SMEs in particular an increased attractiveness as an employer and a competitive advantage in the battle for talent and employee retention.
Exactly this BGM measures lead to health and increased performance. Companies should think very carefully about which measures are up-to-date, effective and, above all, accepted. This is also about evaluating over time and making adjustments where necessary. To do this, it must be precisely defined which goals the health-promoting measures The aim is to track what needs employees have and what period of time is set for an evaluation. This requires a BGM concept that is customised to the company.

As with everything that is introduced in a company, there should be a concept behind it. Without such a concept, many people tend to run off blindly and get lost in the details or give up after a few weeks at the latest. Health is definitely too important for that.
In this concept, it is important to remember that you have to think in several directions in order to really cover all needs. This means that we think in Prevention and in Reaction.
Prevention to prevent absences. The measures are aimed at healthy employees in order to Maintaining health and even systematically strengthen them. This primarily includes health-promoting measures and occupational health and safety measures.
Reaction or reactive measures on the other hand, are aimed at employees who are ill or absent in order to Restore health. This includes company integration management, for example.
Implementation poses a challenge for many companies. On the one hand, measures may have already been introduced that need to be transferred to the new concept. On the other hand, there are new needs and objectives that need to be covered. It therefore makes sense to follow a plan in order to build up the concept in a structured way and achieve long-term and sustainable health.
The first step of the concept is to take stock of the existing structures and processes. So before you start picking out measures, it is important to summarise the existing measures, processes and structures. You can use the following questions as a guide:
In many other models, the objectives are defined first before the analysis of the current situation is carried out. In this model, the two steps are reversed, as this model follows the approach that information gathering comes first before goals can be defined. In the end, however, it is up to you in which order you carry it out.
This is about the current state of your health management. It is no longer about the existing measures, but about hard facts on the health of employees. You can use various analysis methods as a source for this:
Quantitative methods:
Qualitative methods:
In many companies, 100% has still not arrived. It therefore makes sense for many companies to provide the health manager (if there is one) with expert advice. This has two advantages, which are briefly explained here.
The first advantage is that all target groups are heard and measures can be precisely tailored to them. It also makes it easier to evaluate the measures, as direct feedback from the workforce is fed into the Expert Council.
The second major advantage is the involvement of managers and employee representatives. This means that managers are behind it, even motivate employees and pay more attention to their own health.
The following groups of people should be invited to a health circle:

The goals you define for your company are extremely important. Above all, the goal is to Long-term systematic behavioural change to achieve. The individual goals can be set based on the data you have identified in the previous analysis. However, you can also set individual goals that are important to you. However, it is crucial that you involve various stakeholders in the decision. This does not mean that everyone should express their opinion, but that the stakeholders should give their commitment. Above all, the management must be on board so that it works company-wide.
Firstly, you should define strategic goals that are fundamentally important for the company and reduce existing shortcomings. These strategic goals are formulated in rather general terms, such as Reduce staff turnover
You can use various target criteria as a guide:
In the next step, these strategic goals must be converted into operational goals. Operational goals in OHM must always be designed according to the SMART principle. SMART stands for specific, measurable, current, realisable and scheduled. Employees must accept these goals and be able to act accordingly. It therefore makes sense to formulate the goals clearly and communicate them to everyone.
An operational target could therefore be as follows: The fluctuation rate in the company should be reduced from 15% to 10% within the next 3 years.
The saying of implementation consultant Winfried Berner also applies to OHM: You can change almost everything, but not everything at the same time.
It is therefore important to set focal points or priorities in the OHM concept that can be tackled gradually. It also makes sense to look at whether different measures build on each other in order to achieve long-term success. You should note which topics are mandatory and prioritise these if they have not yet been implemented. Legislative changes should also be incorporated on an ad hoc basis.
When it comes to the BGM measures then you should always keep a close eye on the goals. The measures should be selected according to which goals are to be achieved and how much the measure really does to achieve them. Also consider the measures that already exist in the company and add to these in a meaningful way.
A basic distinction is made between the measures in OHM between preventive measures and reactive measures.
Preventive measures are aimed at healthy employees in order to maintain their health and motivation.
Reactive measures are suitable for employees who are ill or demotivated in order to counteract this situation.
Once the measures have been introduced, they must of course be utilised by the employees. There are certainly differences in the participation rate, but this is not surprising as some measures are more and less important to individuals. However, it is invariably important that the Measures monitored/evaluated become. In the best case scenario, you should plan this regularly and make it a fixed routine train. This is the only way you can monitor whether the measures are contributing to the objectives and whether they are really paying off or just causing costs.
As in other areas, you can use so-called KPIs use. This BGM key figures are closely linked to the goals you have set for your company. If we use the example from above, with the aim of reducing staff turnover, we naturally take the staff turnover rate as the KPI and look at the progression of this key figure over time. However, it is important that various parameters are taken into account. If a target is set for the very long term, you should of course not give up straight away. If a target is affected by seasonal fluctuations, these must be taken into account.
For smaller companies, there is also the possibility that BGM concept in 4 steps to develop.
If we think back a few years, the health day was probably the most popular health tool in many companies. However, it was attended less and less, and this has changed completely since coronavirus at the latest. Employees want to keep an eye on their health at all times, both in the office and when working from home. That's why digital health management is becoming increasingly important.
Many BGM providers offer a health app that provides information on sport, nutrition and many other health-related topics. The advantage is broad knowledge and accessibility from anywhere. The disadvantage is an oversupply of irrelevant content and sometimes too little personalisation.
Other providers offer SaaS solutions for mental health, coaching or therapies, for example. This is certainly a very helpful tool for the mental health of employees.
Also brand new AI for use. With the help of AI, a few providers have managed to develop products that respond personally to each employee and are fully customisable. Contribute individually to the improvement of well-being.
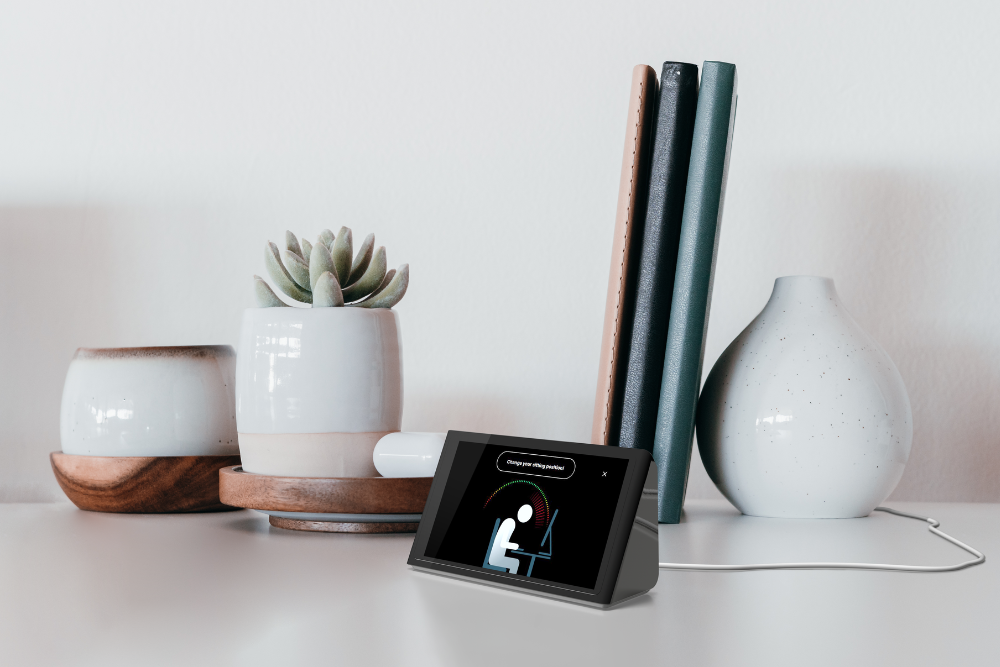

This has the advantage that more employees take part in the BGM measures. On the one hand, because they can use the solution both in the office and when working from home. On the other hand, because a digital solution with AI leads to an individual change in behaviour. In the best-case scenario, employees will no longer need the measures after a few months.
Finally, there is one important question to clarify: How can as much as possible be offered at a low price? However, this question is not as easy to answer as one might think. Most people have heard that WHM is paid for by health insurance companies or that there is a tax-free WHM budget of €600. This is partly true, but only partly.
In principle, you can pursue BGM with any budget. So don't give up straight away if the budget is not so high. The important thing is that many things can be done internally and therefore only the personnel costs are incurred. For external solutions, of course, some budget must be made available. However, there are also solutions ranging from cheap to expensive. For large companies, the bouquet of measures can quickly swallow up six-figure sums. For a smaller company, you should reckon with around €10,000.
You can find out which measures cost how much in our article: BGM costs: financing, funding and ROI
However, health is not only important for companies and their employees, but also for Germany's economic performance and spending in general. This is why German legislators are also keen to promote this issue further. Statutory health insurance companies for example, are obliged to invest a fixed amount (at least €3.15) per insured person per year in workplace health promotion. This obligation is set out in the Prevention Act (PrävG §20 SGB V). You can obtain further information on this from your health insurance company.
However, the legislator itself is also investing in the health of the population. For example, companies can pay up to 600€ per year tax-free for BGM measuresthat fulfil the requirements of §§20 and 20b SGB V. This includes benefits such as individual behaviour-related prevention, prevention courses provided by the employer (if certain requirements are met) and other benefits. You can find out more details from your tax consultant or legal advisor.
OHM is a very important topic and will become increasingly important in the future. It not only supports companies in the area of employee health, but also serves to motivate and retain employees. In this way, companies offer added value that gives them a competitive advantage in the labour market.
A successful OHM certainly involves a lot of investment, but it is an investment in the present and the future of the company.
Occupational health and safety and integration management are mandatory components, whereas health promotion is voluntary. However, this does not mean that one of these pillars is less important than the others. A good mix is the key to success.
Digital solutions are particularly suitable for this, in the best case even AI-supported solutions. These are more flexible in terms of time and place and are more customised to the needs of the individual.
Thanks to subsidies from health insurance companies and the state, OHM can even be implemented relatively inexpensively. But as I said, the investments that companies make here are important investments with a high return on investment. Nowadays, OHM is no longer a "nice to have", but a "must have" for a better future.